Filter device: 10μm filter cotton/can be cleaned 10μm filter
Atomized particles: dispersed in the air fog particles less than 50um, in the air can reach the suspension state and then falling
Liquid requirements: Under high pressure, there will be residual exotics and impurities in the liquid. It must be added to the pure water filter to achieve the purity similar to household drinking water before it can be introduced into the impingement fog nozzle
Typical application: the impingement fog nozzle can be widely used in workshop humidification, man-made, livestock farms, greenhouse and man-made landscape and other need to apply humidification spray occasions
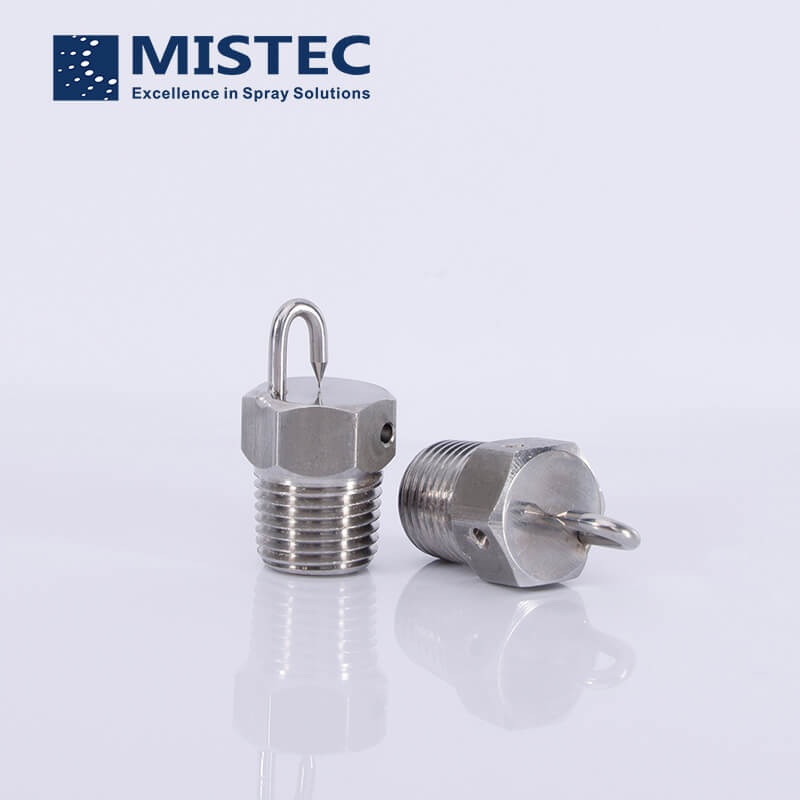
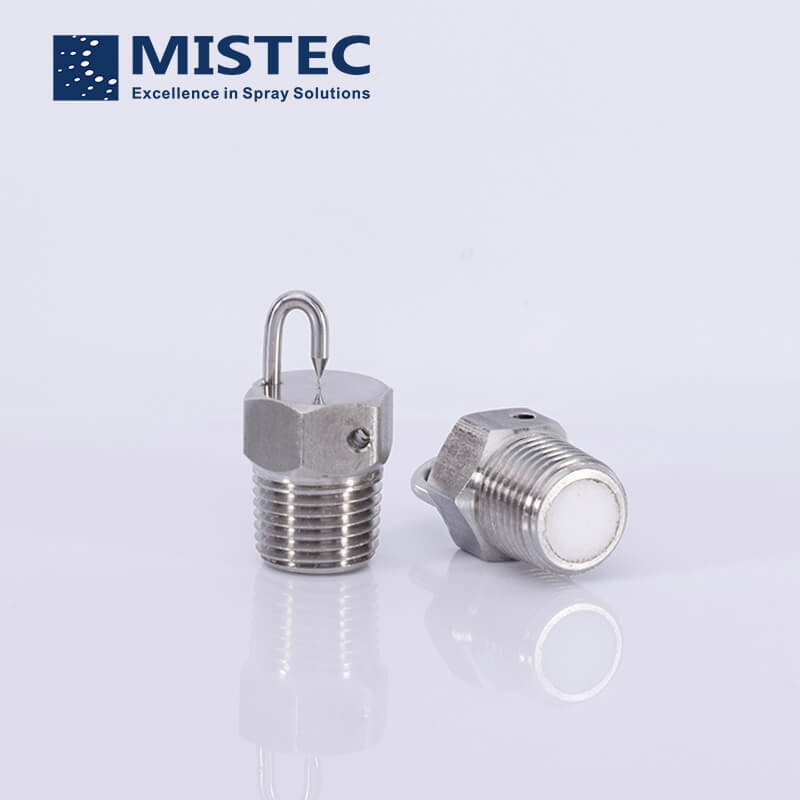
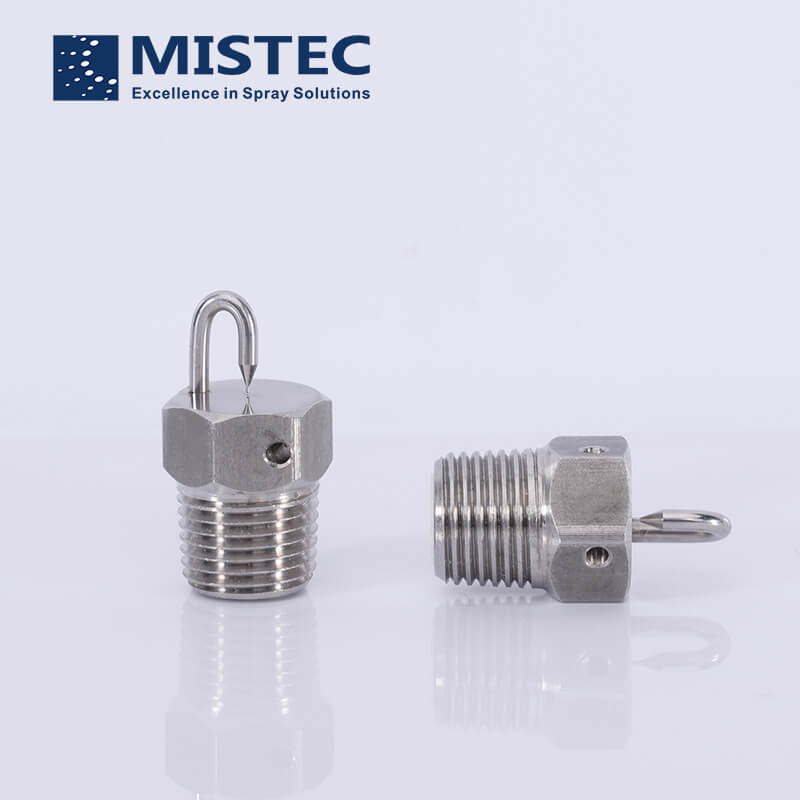
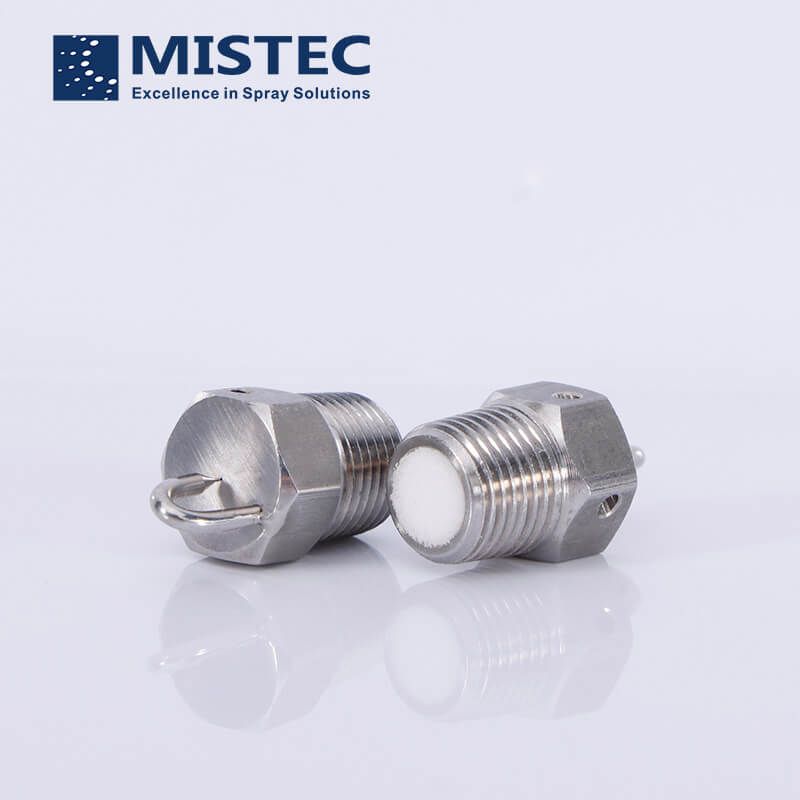
The the impingement fog nozzle is composed of a frame, a thimble and a splashing tray. The working principle of the impingement fog nozzle is that the liquid column sprayed out of the spray hole hits the diameter of the spray hole opposite it, and the target needle with the same aperture, and then slowly forms a very fine atomization effect. The fine water sprayed to the splash tray is ejected from the nozzle to form a spray, which is the operating characteristic of the impingement fog nozzle.
Fire extinguishing mechanism of foam fire extinguishing system
The fire extinguishing mechanism of the foam fire extinguishing system is oxygen insulation, radiation heat insulation and endothermic cooling. Foam fire extinguishing system is mainly used to extinguish insoluble flammable liquid and general solid fire. The fire extinguishing principle is that the aqueous solution of the foam fire extinguishing agent fills a large amount of gas (CQ, air) through chemical and physical effects to form numerous small bubbles, covering the surface of the combustion, so that the combustion is isolated from the air, blocking the thermal radiation of the flame, so as to form the fire extinguishing ability. At the same time, the foam precipitates liquid during the fire extinguishing process, which can cool the combustion. The water vapor generated by heat can also reduce the oxygen concentration near the combustion material, and can also play a better fire extinguishing effect.
The difference between the application field of high, medium and low expansion foam fire extinguishing system
1. Low expansion foam fire extinguishing system
1. The main parts of the low-expansion foam fire extinguishing system are: fire pump, pressure type foam proportional mixing device, low-expansion air foam generator, rain valve, and other valves and pipe fittings.
2, the fire extinguishing principle through the pressure type proportional mixing device to mix water and foam extinguishing agent, forming a certain proportion of foam mixture, through the foam generator to inhale air to form foam, foam nozzle down the tank wall, covering the burning liquid, so as to extinguish the fire.
3, the scope of application low expansion foam fire extinguishing system is suitable for processing, storage, loading and unloading, the use of A (except liquefied hydrocarbons), B, C liquid places. Such as: oil fields, refineries, chemical plants, docks, underground garages, hangars, airports, fuel boiler rooms and other places.
Second, medium multiple, high multiple foam fire extinguishing system
1, the composition of medium multiple, high multiple foam fire extinguishing system is mainly composed of fire pump, pressure proportional mixing device, foam generator, valve, pipeline and so on.
2, fire extinguishing principle with the advantage of the large amount of foam, although the thermal stability of medium and high multiple foam is slightly poor, the foam is easily damaged by the flame and affected by the outdoor natural wind, but the amount of foam generated per unit time is far greater than the amount of foam destruction, so that it can quickly fill the burning space and extinguish the flame.
3, application range, high expansion foam fire extinguishing system is suitable for fighting class A, Class B fire, limited enclosed space fire, control liquefied petroleum gas, liquefied natural gas flowing fire. Such as: solid material warehouses, flammable liquid warehouses, industrial plants with fire hazards, underground construction projects, engine rooms, pump rooms, cargo holds of various ships, valuable instruments and equipment and substances, flammable flammable liquids and liquefied petroleum gas and liquefied natural gas flowing fires.


















.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)